GeoMesa FileSystem Quick Start¶
This tutorial is the fastest and easiest way to get started with GeoMesa using the FileSytem data store (FSDS). The FSDS lets you store and query data without any database instance, using flat files. These files can be stored in HDFS, AWS, or even your local disk.
It is a good stepping-stone on the path to the other tutorials, that present increasingly involved examples of how to use GeoMesa.
About this Tutorial¶
In the spirit of keeping things simple, the code in this tutorial only does a few small things:
Establishes a new (static) SimpleFeatureType
Prepares the file system to store this type of data
Creates a few thousand example SimpleFeatures
Writes these SimpleFeatures to the file system
Queries for a given geographic rectangle, time range, and attribute filter, writing out the entries in the result set
Uses GeoServer to visualize the data (optional)
Prerequisites¶
Before you begin, you must have the following installed and configured:
Download and Build the Tutorial¶
Pick a reasonable directory on your machine, and run:
$ git clone https://github.com/geomesa/geomesa-tutorials.git
$ cd geomesa-tutorials
Warning
Make sure that you download or checkout the version of the tutorials project that corresponds to your GeoMesa version. See About Tutorial Versions for more details.
To ensure that the quick start works with your environment, modify the pom.xml
to set the appropriate versions for Hadoop, etc.
For ease of use, the project builds a bundled artifact that contains all the required dependencies in a single JAR. To build, run:
$ mvn clean install -pl geomesa-tutorials-fsds/geomesa-tutorials-fsds-quickstart -am
Running the Tutorial¶
On the command line, run:
$ java -cp geomesa-tutorials-fsds/geomesa-tutorials-fsds-quickstart/target/geomesa-tutorials-fsds-quickstart-$VERSION.jar \
org.geomesa.example.fsds.FileSystemQuickStart \
--fs.path /tmp/fsds/ \
--fs.encoding parquet
The arguments above indicate:
fs.paththe FSDS storage path. Each simple feature type will produce a sub-directory here.fs.encodingthe file storage encoding. The quick start comes pre-configured to use Apache’s Parquet encoding.
Once run, you should see the following output:
Loading datastore
Creating schema: GLOBALEVENTID:String,Actor1Name:String,Actor1CountryCode:String,Actor2Name:String,Actor2CountryCode:String,EventCode:String,NumMentions:Integer,NumSources:Integer,NumArticles:Integer,ActionGeo_Type:Integer,ActionGeo_FullName:String,ActionGeo_CountryCode:String,dtg:Date,geom:Point:srid=4326
Generating test data
Writing test data
Wrote 2356 features
Running test queries
Running query BBOX(geom, -120.0,30.0,-75.0,55.0) AND dtg DURING 2017-12-31T00:00:00+00:00/2018-01-02T00:00:00+00:00
01 719024913=719024913|||VICTORIA|AUS|173|2|1|2|4|Victoria Harbour, Ontario, Canada|CA|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-79.7667 44.75)
02 719024918=719024918|||EMPLOYER||020|10|1|10|3|Brooklyn, New York, United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-75.1704 42.3442)
03 719024923=719024923|||INDUSTRY||084|3|1|3|2|Pennsylvania, United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-77.264 40.5773)
04 719024924=719024924|||CORPORATION||115|2|1|2|4|Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada|CA|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-106.667 52.1333)
05 719024925=719024925|||CORPORATION||172|2|1|2|4|Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada|CA|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-106.667 52.1333)
06 719024927=719024927|||CANADIAN|CAN|100|24|2|14|4|Ottawa, Ontario, Canada|CA|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-75.7 45.4167)
07 719024928=719024928|||CANADIAN|CAN|100|6|1|6|1|United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-98.5795 39.828175)
08 719024929=719024929|||CANADA|CAN|190|4|1|4|4|Okanagan, British Columbia, Canada|CA|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-119.35 50.3667)
09 719024933=719024933|||POLICE||020|48|12|24|3|Wichita, Kansas, United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-97.3375 37.6922)
10 719024934=719024934|||POLICE||036|10|1|10|3|Bosque County, Texas, United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-97.6503 31.9002)
Returned 669 total features
Running query BBOX(geom, -120.0,30.0,-75.0,55.0) AND dtg DURING 2017-12-31T00:00:00+00:00/2018-01-02T00:00:00+00:00
Returning attributes [GLOBALEVENTID, dtg, geom]
01 719024913=719024913|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-79.7667 44.75)
02 719024918=719024918|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-75.1704 42.3442)
03 719024923=719024923|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-77.264 40.5773)
04 719024924=719024924|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-106.667 52.1333)
05 719024925=719024925|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-106.667 52.1333)
06 719024927=719024927|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-75.7 45.4167)
07 719024928=719024928|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-98.5795 39.828175)
08 719024929=719024929|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-119.35 50.3667)
09 719024933=719024933|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-97.3375 37.6922)
10 719024934=719024934|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-97.6503 31.9002)
Returned 669 total features
Running query EventCode = '051'
01 719024909=719024909|||MELBOURNE|AUS|051|10|1|10|4|Melbourne, Victoria, Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (144.967 -37.8167)
02 719024963=719024963|||CITIZEN||051|6|2|6|4|City Of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
03 719025168=719025168|AUSTRALIAN|AUS|||051|18|1|10|4|Sydney, New South Wales, Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
04 719025178=719025178|AUSTRALIA|AUS|COMMUNITY||051|20|2|20|4|Sydney, New South Wales, Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
05 719025248=719025248|BUSINESS||||051|10|1|10|1|Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
06 719025509=719025509|COMMUNITY||AUSTRALIA|AUS|051|2|1|2|1|Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
07 719025555=719025555|DENMARK|DNK|||051|2|1|2|1|Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
08 719025634=719025634|FIJI|FJI|||051|2|1|2|1|Fiji|FJ|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (178 -18)
09 719025965=719025965|MIDWIFE||||051|10|1|10|4|Sydney, New South Wales, Australia|AS|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
10 719025036=719025036|||SENATE||051|5|1|5|2|Alabama, United States|US|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (-86.8073 32.799)
Returned 138 total features
Running query EventCode = '051' AND dtg DURING 2017-12-31T00:00:00+00:00/2018-01-02T00:00:00+00:00
Returning attributes [GLOBALEVENTID, dtg, geom]
01 719024909=719024909|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (144.967 -37.8167)
02 719024963=719024963|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
03 719025168=719025168|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
04 719025178=719025178|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
05 719025248=719025248|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
06 719025509=719025509|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
07 719025555=719025555|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (135 -25)
08 719025634=719025634|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (178 -18)
09 719025965=719025965|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (151.217 -33.8833)
10 719024994=719024994|2018-01-01T00:00:00.000Z|POINT (79.25 30.25)
Returned 138 total features
Cleaning up test data
Done
Looking at the Code¶
The source code is meant to be accessible for this tutorial. The main logic is contained in
the generic org.geomesa.example.quickstart.GeoMesaQuickStart in the geomesa-tutorials-common module,
which is datastore agnostic. Some relevant methods are:
createDataStoreget a datastore instance from the input configurationcreateSchemacreate the schema in the datastore, as a pre-requisite to writing datawriteFeaturesuse aFeatureWriterto write features to the datastorequeryFeaturesrun several queries against the datastorecleanupdelete the datastore directory and dispose of the datastore instance.
The quick start uses a small subset of GDELT data. Code for parsing the data into GeoTools SimpleFeatures is
contained in org.geomesa.example.data.GDELTData:
getSimpleFeatureTypecreates theSimpleFeatureTyperepresenting the datagetTestDataparses an embedded TSV file to createSimpleFeatureobjectsgetTestQueriesillustrates several different query types, using CQL (GeoTools’ Contextual Query Language)
Visualize Data (optional)¶
There are two options to visual the data ingested by this quick start. The easiest option is to use the
export command of the GeoMesa FSDS tools distribution. For a more production ready example, you can
alternatively stand up a GeoServer and connect it to your FSDS instance.
Visualize Data With Leaflet¶
Warning
To successfully run this command you must have a computer that is connected to the internet in order to access external Leaflet resources.
The export command is a part of the GeoMesa FSDS command-line tools. In order to use the command,
ensure you have the command-line tools installed as described in Setting up the FileSystem Command Line Tools.
The export command provides the leaflet format which will export the features to a Leaflet map
that you can open in your web browser. To produce the map, run the following command from the GeoMesa
FSDS tools distribution directory:
bin/geomesa-fs export \
--feature-name gdelt-quickstart \
--output-format leaflet \
--path /tmp/fsds/
Where the connection parameters are the same you used above during the quickstart. To view the map simply open the url provided by the command in your web browser. If you click the menu in the upper right of the map you can enable and disable the heatmap and feature layers as well as the two provided base layers.
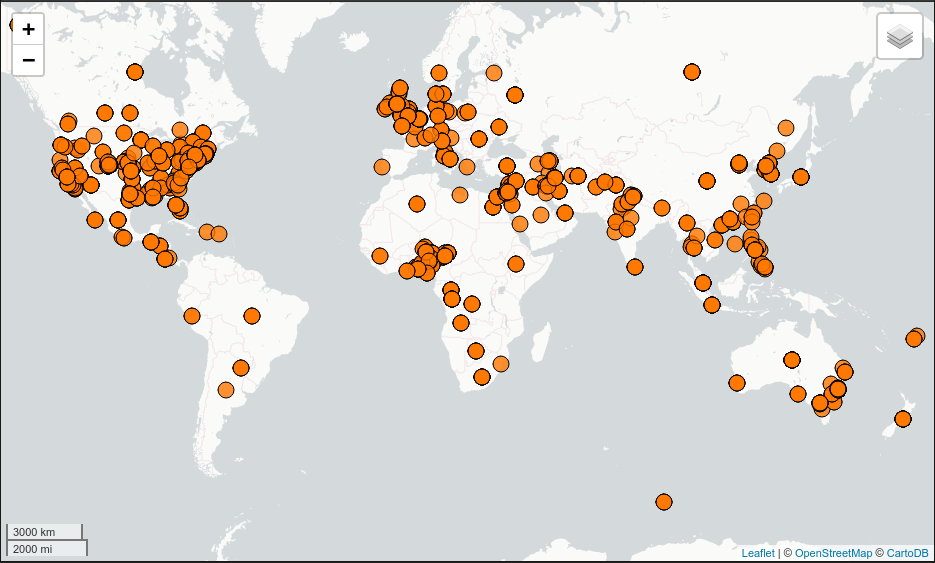
Visualizing quick-start data with Leaflet¶
Visualize Data With GeoServer¶
You can use GeoServer to access and visualize the data stored in GeoMesa. In order to use GeoServer, download and install version 2.27.1. Then follow the instructions in Installing GeoMesa FileSystem in GeoServer to enable GeoMesa.
Register the GeoMesa Store with GeoServer¶
Log into GeoServer using your user and password credentials. Click
“Stores” and “Add new Store”. Select the FileSystem (GeoMesa) vector data
source, and fill in the required parameters.
Basic store info:
workspacethis is dependent upon your GeoServer installationdata source namepick a sensible name, such asgeomesa_quick_startdescriptionthis is strictly decorative;GeoMesa quick start
Connection parameters:
these are the same parameter values that you supplied on the command line when you ran the tutorial; they describe how to connect to the FSDS location where your data reside
Click “Save”, and GeoServer will search your FSDS directory for any GeoMesa-managed feature types.
Publish the Layer¶
GeoServer should recognize the gdelt-quickstart feature type, and
should present that as a layer that can be published. Click on the
“Publish” link.
You will be taken to the “Edit Layer” screen. You will need to enter values for the data bounding boxes. In this case, you can click on the link to compute these values from the data.
Click on the “Save” button when you are done.
Take a Look¶
Click on the “Layer Preview” link in the left-hand gutter. If you don’t
see the quick-start layer on the first page of results, enter the name
of the layer you just created into the search box, and press
<Enter>.
Once you see your layer, click on the “OpenLayers” link, which will open a new tab. You should see a collection of red dots similar to the following image:
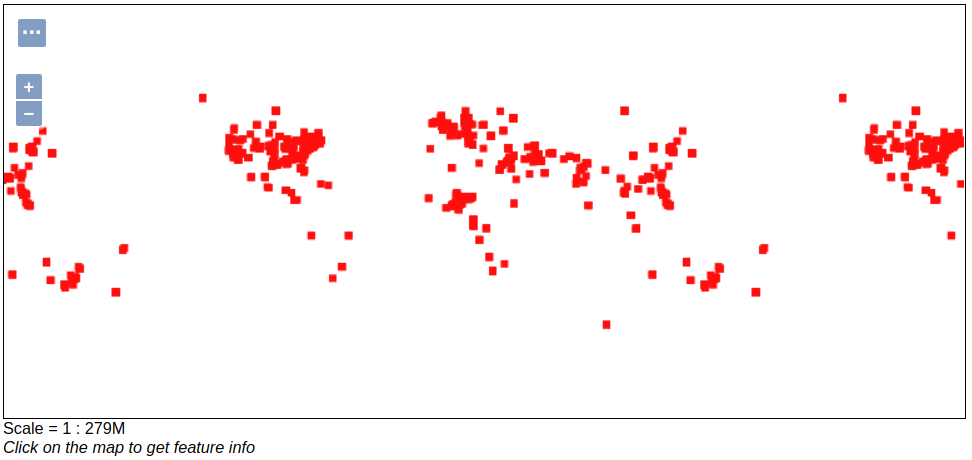
Visualizing quick-start data with GeoServer¶
Tweaking the display¶
Here are just a few simple ways you can play with the visualization:
Click on one of the red points in the display, and GeoServer will report the detail records underneath the map area.
Shift-click to highlight a region within the map that you would like to zoom into.
Click on the “Toggle options toolbar” icon in the upper-left corner of the preview window. The right-hand side of the screen will include a “Filter” text box. Enter
EventCode = '051', and press on the “play” icon. The display will now show only those points matching your filter criterion. This is a CQL filter, which can be constructed in various ways to query your data. You can find more information about CQL from GeoServer’s CQL tutorial.